ClimaX
ClimaX is a foundation model designed to be pre-trained on heterogeneous data sources and then fine-tuned to solve various downstream weather and climate problems.
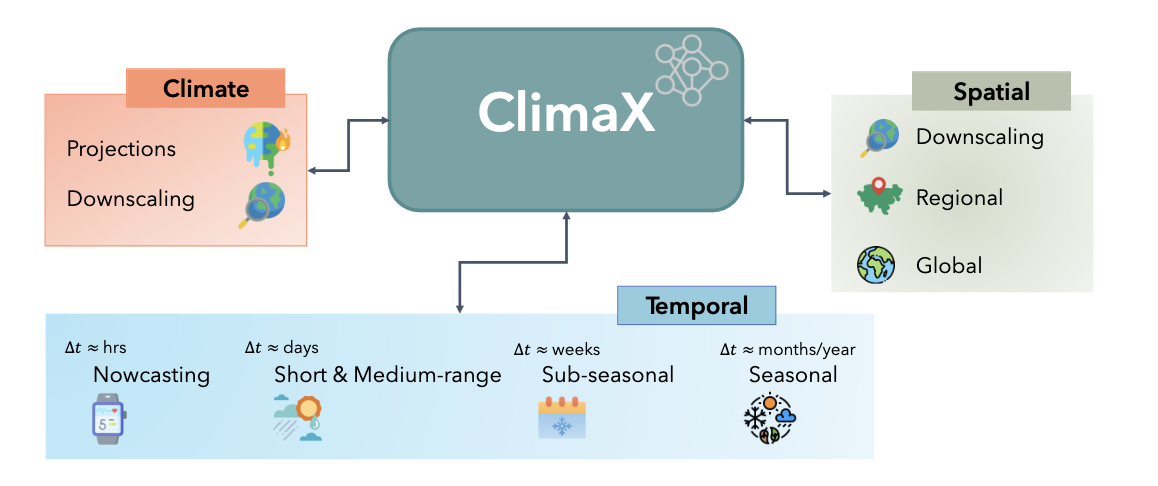
The set of climate and weather variables is extremely broad, and predictions may be required for regional or even spatially incomplete data, even at different resolutions. Current CNN-based architectures are not applicable in these scenarios, as they require the input to be perfectly gridded, contain a fixed set of variables, and have a fixed spatial resolution. resolution. Transformer-based architectures, on the other hand, offer much greater flexibility by treating the image-like data as a set of tokens. As a consequence, the backbone architecture chosen is a Vision Transformer to provide greater flexibility.
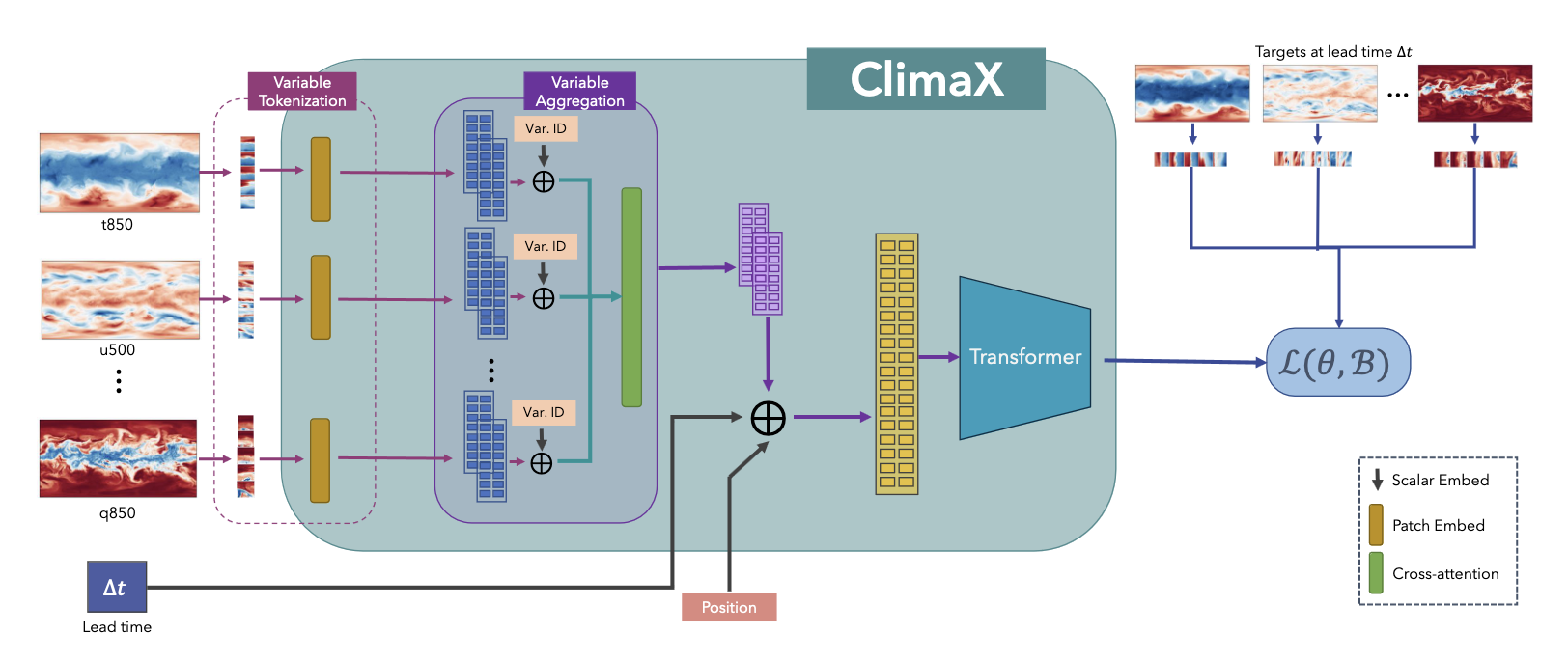
Two significant changes to this model were implemented. The first change involved variable tokenization, which includes separating each variable into its own channel and tokenizing the input into a sequence of patches. The second change was variable aggregation, introduced to speed up computation by reducing the dimensionality of the input data and to aid in distinguishing between different variables, thereby enhancing attention-based training. After combining variables, the vision transformer block can produce output tokens that are then processed through a linear prediction head to recreate the original image. During the pre-training phase, a latitude-weighted reconstruction error is used to keep into account the location of the current patch. For fine-tuning, the ClimaX modules can be frozen, allowing for training only on the intended part of the architecture. In fact, often only the final prediction head and variable coding modules need retraining. This model has undergone testing for several downstream tasks, including global and regional forecasting and prediction for unseen climate tasks.